本文基于 Dubbo 2.6.1 版本,望知悉。
友情提示,【配置】这块的内容,会相对比较枯燥。所以,如果看到一些很难懂的地方,建议先跳过。
对于 Dubbo ,重点是要去理解,多协议、RPC、容错等等模块,而不是【配置】。
😈 估计好多胖友被【配置】这章劝退了把???
1. 概述
本文接 《API 配置(一)之应用》 ,分享服务提供者相关的配置:包括 provider-config 和 sub-config 部分。
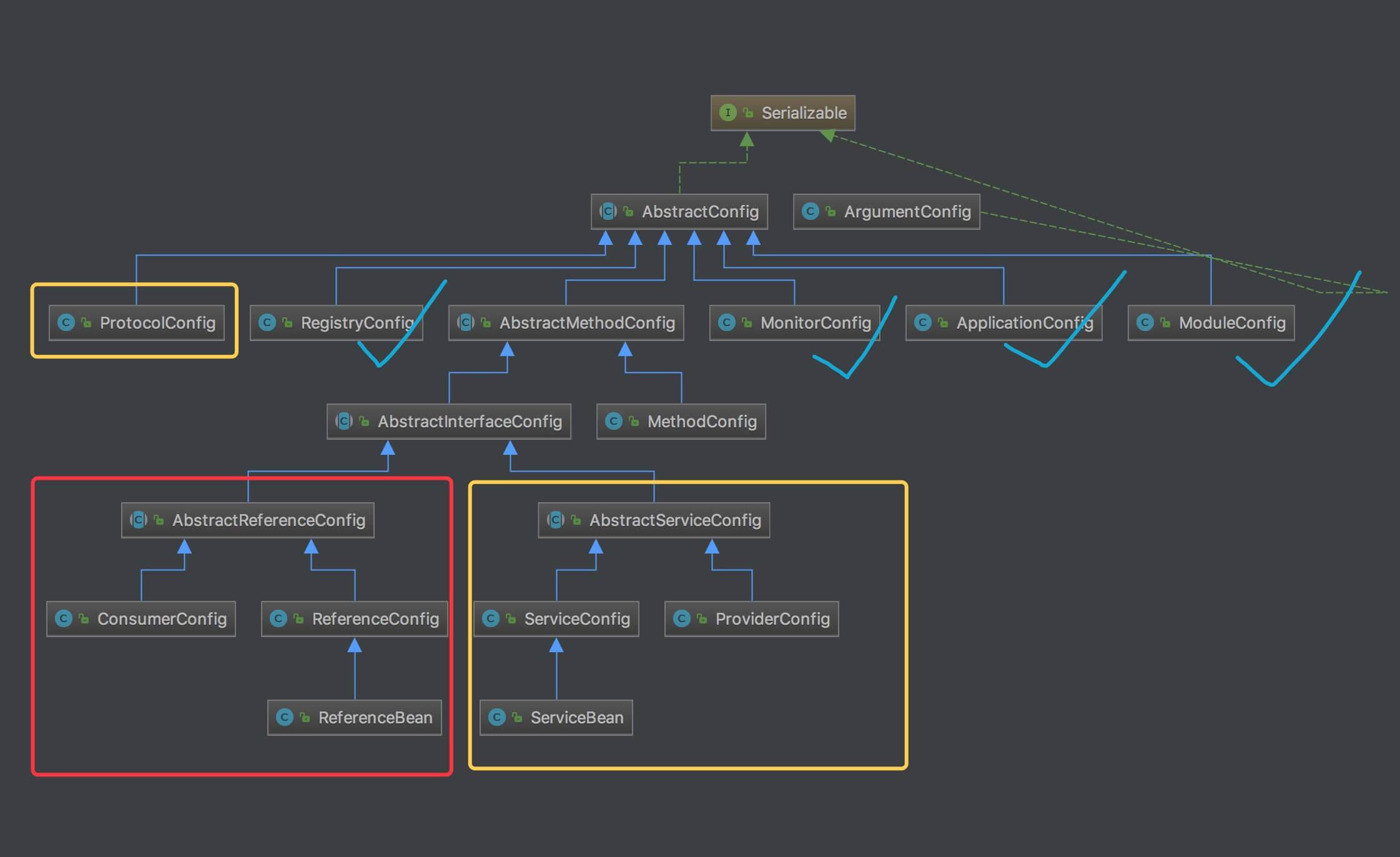
黄框部分,provider-side
其他部分,sub-config
还是老样子,我们先来看一段 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— API 配置》 ,服务提供者的初始化代码:
相比 ReferenceConfig 的初始化,会多创建 ProtocolConfig 对象,设置到 ServiceConfig 对象中。
友情提示:本文前面部分会比较琐碎,重点在 「8. ServiceConfig」 部分。
2. ProtocolConfig
com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ProtocolConfig ,服务提供者协议配置。
具体属性的解释,参见 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:protocol》 文档。
3. AbstractMethodConfig
com.alibaba.dubbo.config.AbstractMethodConfig ,方法级配置的抽象类。
部分属性的解释,参见 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:method》 文档。
4. MethodConfig
com.alibaba.dubbo.config.MethodConfig ,继承 AbstractMethodConfig ,方法级配置。
具体属性的解释,《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:method》 文档。
5. AbstractInterfaceConfig
com.alibaba.dubbo.config.AbstractInterfaceConfig ,继承 AbstractMethodConfig ,抽象接口配置类。
具体属性的解释,需要寻找在 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:service》 或 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:reference》 文档。
下面的方法,会在 「8. ServiceConfig」 的初始化被调用,胖友可需要的时候,点击查看。
#checkApplication()方法,校验 ApplicationConfig 配置。实际上,该方法会初始化 ApplicationConfig 的配置属性。🙂 直接点击方法查看,较为简单,已经添加详细注释。
#checkRegistry()方法,校验 RegistryConfig 配置。实际上,该方法会初始化 RegistryConfig 的配置属性。🙂 直接点击方法查看,较为简单,已经添加详细注释。
#checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods)方法,校验接口和方法。主要是两方面:1、 接口类非空,并是接口
2、 方法在接口中已定义
🙂 直接点击方法查看,较为简单,已经添加详细注释。
#checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass)方法,校验 Stub 和 Mock 相关的配置。以上未列举的
#loadRegistries(provider)和#loadMonitor(registryURL)方法,在后续文章需要使用到时,在详细分享。
6. AbstractServiceConfig
com.alibaba.dubbo.config.AbstractServiceConfig ,实现 AbstractInterfaceConfig ,抽象服务配置类。
具体属性的解释,需要寻找在 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:service》 或 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:provider》 文档。
7. ProviderConfig
com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ProviderConfig ,实现 AbstractServiceConfig ,服务提供者缺省值配置。
具体属性的解释,参见 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:provider》 文档。
8. ServiceConfig
com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig ,服务提供者暴露服务配置类。
具体属性的解释,参见 《Dubbo 用户指南 —— dubbo:service》 文档。
下面,我们进入正戏。
在文初的 ServiceConfig 的初始化示例代码中,最后调用的是 ServiceConfig#export() 方法。从方法的命名,我们可以看出,暴露服务。该方法主要做了如下几件事情:
进一步初始化 ServiceConfig 对象。
校验 ServiceConfig 对象的配置项。
使用 ServiceConfig 对象,生成 Dubbo URL 对象数组。
使用 Dubbo URL 对象,暴露服务。
😈 本文重点在服务提供者相关的配置,因此只解析 1+2+3 部分( 不包括 4 )。代码如下
1: public synchronized void export() {
2: // 当 export 或者 delay 未配置,从 ProviderConfig 对象读取。
3: if (provider != null) {
4: if (export == null) {
5: export = provider.getExport();
6: }
7: if (delay == null) {
8: delay = provider.getDelay();
9: }
10: }
11: // 不暴露服务( export = false ) ,则不进行暴露服务逻辑。
12: if (export != null && !export) {
13: return;
14: }
15:
16: // 延迟暴露
17: if (delay != null && delay > 0) {
18: delayExportExecutor.schedule(new Runnable() {
19: public void run() {
20: doExport();
21: }
22: }, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
23: // 立即暴露
24: } else {
25: doExport();
26: }
27: }第 2 至 10 行:当
export或delay未配置时,从 ProviderConfig 对象读取。第 11 至 14 行:当配置不需要暴露服务(
export = false)时,直接返回。第 17 至 22 行:当配置延迟暴露(
delay > 0)时,使用delayExportExecutor延迟调度,调用#doExport()方法。第 23 至 26 行:立即暴露,调用
#doExport()方法。
#doExport() 方法,代码如下:
1: protected synchronized void doExport() {
2: // 检查是否可以暴露,若可以,标记已经暴露。
3: if (unexported) {
4: throw new IllegalStateException("Already unexported!");
5: }
6: if (exported) {
7: return;
8: }
9: exported = true;
10: // 校验接口名非空
11: if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) {
12: throw new IllegalStateException("<dubbo:service interface=\"\" /> interface not allow null!");
13: }
14: // 拼接属性配置(环境变量 + properties 属性)到 ProviderConfig 对象
15: checkDefault();
16: // 从 ProviderConfig 对象中,读取 application、module、registries、monitor、protocols 配置对象。
17: if (provider != null) {
18: if (application == null) {
19: application = provider.getApplication();
20: }
21: if (module == null) {
22: module = provider.getModule();
23: }
24: if (registries == null) {
25: registries = provider.getRegistries();
26: }
27: if (monitor == null) {
28: monitor = provider.getMonitor();
29: }
30: if (protocols == null) {
31: protocols = provider.getProtocols();
32: }
33: }
34: // 从 ModuleConfig 对象中,读取 registries、monitor 配置对象。
35: if (module != null) {
36: if (registries == null) {
37: registries = module.getRegistries();
38: }
39: if (monitor == null) {
40: monitor = module.getMonitor();
41: }
42: }
43: // 从 ApplicationConfig 对象中,读取 registries、monitor 配置对象。
44: if (application != null) {
45: if (registries == null) {
46: registries = application.getRegistries();
47: }
48: if (monitor == null) {
49: monitor = application.getMonitor();
50: }
51: }
52: // 泛化接口的实现
53: if (ref instanceof GenericService) {
54: interfaceClass = GenericService.class;
55: if (StringUtils.isEmpty(generic)) {
56: generic = Boolean.TRUE.toString();
57: }
58: // 普通接口的实现
59: } else {
60: try {
61: interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
62: } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
63: throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
64: }
65: // 校验接口和方法
66: checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods);
67: // 校验指向的 service 对象
68: checkRef();
69: generic = Boolean.FALSE.toString();
70: }
71: // 处理服务接口客户端本地代理( `local` )相关。实际目前已经废弃,使用 `stub` 属性,参见 `AbstractInterfaceConfig#setLocal` 方法。
72: if (local != null) {
73: // 设为 true,表示使用缺省代理类名,即:接口名 + Local 后缀
74: if ("true".equals(local)) {
75: local = interfaceName + "Local";
76: }
77: Class<?> localClass;
78: try {
79: localClass = ClassHelper.forNameWithThreadContextClassLoader(local);
80: } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
81: throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
82: }
83: if (!interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(localClass)) {
84: throw new IllegalStateException("The local implementation class " + localClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + interfaceName);
85: }
86: }
87: // 处理服务接口客户端本地代理( `stub` )相关
88: if (stub != null) {
89: // 设为 true,表示使用缺省代理类名,即:接口名 + Stub 后缀
90: if ("true".equals(stub)) {
91: stub = interfaceName + "Stub";
92: }
93: Class<?> stubClass;
94: try {
95: stubClass = ClassHelper.forNameWithThreadContextClassLoader(stub);
96: } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
97: throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
98: }
99: if (!interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(stubClass)) {
100: throw new IllegalStateException("The stub implementation class " + stubClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + interfaceName);
101: }
102: }
103: // 校验 ApplicationConfig 配置。
104: checkApplication();
105: // 校验 RegistryConfig 配置。
106: checkRegistry();
107: // 校验 ProtocolConfig 配置数组。
108: checkProtocol();
109: // 读取环境变量和 properties 配置到 ServiceConfig 对象。
110: appendProperties(this);
111: // 校验 Stub 和 Mock 相关的配置
112: checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass);
113: // 服务路径,缺省为接口名
114: if (path == null || path.length() == 0) {
115: path = interfaceName;
116: }
117: // 暴露服务
118: doExportUrls();
119: // TODO,等待 qos
120: ProviderModel providerModel = new ProviderModel(getUniqueServiceName(), this, ref);
121: ApplicationModel.initProviderModel(getUniqueServiceName(), providerModel);
122: }第 2 至 9 行:检查是否可以暴露。若可以,标记已经暴露(
exported = true)。第 10 至 13 行:校验接口名
interfaceName非空。第 15 行:调用
#checkDefault()方法,读取属性配置( 环境变量 + properties 属性 )到 ProviderConfig 对象。关于“属性配置” ,在 《精尽 Dubbo 源码解析 —— 属性配置》 详细解析。
🙂 直接点击方法查看,较为简单,已经添加详细注释。
第 16 至 33 行:从 ProviderConfig 对象中,读取
application、module、registries、monitor、protocols对象。第 34 至 42 行:从 ModuleConfig 对象中,读取
registries、monitor对象。第 43 至 51 行:从 ApplicationConfig 对象中,读取
registries、monitor对象。第 52 至 57 行:泛化接口的实现。
第 58 至 70 行:普通接口的实现。
第 60 至 64 行:根据
interfaceName,获得对应的接口类,并赋值给interfaceClass。第 66 行:调用
#checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods)方法,检查接口和方法。🙂 本文有已经有这个方法的解析。
第 68 行:调用
#checkRef()方法,校验指向的 Service 对象。第 69 行:标记
generic为非泛化实现。
第 71 至 86 行:处理服务接口客户端本地代理(
local)相关。实际目前已经废弃,此处主要用于兼容,使用stub属性,参见AbstractInterfaceConfig#setLocal(local)方法的注释说明。第 87 至 102 行:处理服务接口客户端本地代理(
stub属性,参见AbstractInterfaceConfig#setLocal(local))相关。第 104 行:调用
#checkApplication()方法,校验 ApplicationConfig 配置。🙂 直接点击方法查看,较为简单,已经添加详细注释。
第 106 行:调用
#checkRegistry()方法,校验 RegistryConfig 配置。🙂 直接点击方法查看,较为简单,已经添加详细注释。
第 108 行:调用
#checkProtocol()方法,校验 ProtocolConfig 配置数组。🙂 直接点击方法查看,较为简单,已经添加详细注释。
第 110 行:调用
#appendProperties(config)方法,读取属性配置( 环境变量 + properties 属性 )到 ServiceConfig 对象(自己)。第 112 行:调用
#checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass)方法,校验 Stub 和 Mock 相关的配置。第 113 至 116 行:服务路径
path为空时,缺省为接口名。第 118 行:调用
#doExportUrls()方法,暴露服务。此方法包含了我们上述的 3+4 部分。第 119 至 121 行:// TODO ,等待 qos
因为本文不分享 4 部分,所以下面我们只看 #doExportUrls() 方法中,调用 #doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(protocolConfig, registryURLs) 方法,和 3 有关的部分。代码如下:
1: private void doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(ProtocolConfig protocolConfig, List<URL> registryURLs) {
2: // 协议名
3: String name = protocolConfig.getName();
4: if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
5: name = "dubbo";
6: }
7:
8: // 将 `side`,`dubbo`,`timestamp`,`pid` 参数,添加到 `map` 集合中。
9: Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
10: map.put(Constants.SIDE_KEY, Constants.PROVIDER_SIDE);
11: map.put(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, Version.getVersion());
12: map.put(Constants.TIMESTAMP_KEY, String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()));
13: if (ConfigUtils.getPid() > 0) {
14: map.put(Constants.PID_KEY, String.valueOf(ConfigUtils.getPid()));
15: }
16: // 将各种配置对象,添加到 `map` 集合中。
17: appendParameters(map, application);
18: appendParameters(map, module);
19: appendParameters(map, provider, Constants.DEFAULT_KEY); // ProviderConfig ,为 ServiceConfig 的默认属性,因此添加 `default` 属性前缀。
20: appendParameters(map, protocolConfig);
21: appendParameters(map, this);
22: // 将 MethodConfig 对象数组,添加到 `map` 集合中。
23: if (methods != null && !methods.isEmpty()) {
24: for (MethodConfig method : methods) {
25: // 将 MethodConfig 对象,添加到 `map` 集合中。
26: appendParameters(map, method, method.getName());
27: // 当 配置了 `MethodConfig.retry = false` 时,强制禁用重试
28: String retryKey = method.getName() + ".retry";
29: if (map.containsKey(retryKey)) {
30: String retryValue = map.remove(retryKey);
31: if ("false".equals(retryValue)) {
32: map.put(method.getName() + ".retries", "0");
33: }
34: }
35: // 将 ArgumentConfig 对象数组,添加到 `map` 集合中。
36: List<ArgumentConfig> arguments = method.getArguments();
37: if (arguments != null && !arguments.isEmpty()) {
38: for (ArgumentConfig argument : arguments) {
39: // convert argument type
40: if (argument.getType() != null && argument.getType().length() > 0) { // 指定了类型
41: Method[] methods = interfaceClass.getMethods();
42: // visit all methods
43: if (methods != null && methods.length > 0) {
44: for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
45: String methodName = methods[i].getName();
46: // target the method, and get its signature
47: if (methodName.equals(method.getName())) { // 找到指定方法
48: Class<?>[] argTypes = methods[i].getParameterTypes();
49: // one callback in the method
50: if (argument.getIndex() != -1) { // 指定单个参数的位置 + 类型
51: if (argTypes[argument.getIndex()].getName().equals(argument.getType())) {
52: // 将 ArgumentConfig 对象,添加到 `map` 集合中。
53: appendParameters(map, argument, method.getName() + "." + argument.getIndex()); // `${methodName}.${index}`
54: } else {
55: throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument config error : the index attribute and type attribute not match :index :" + argument.getIndex() + ", type:" + argument.getType());
56: }
57: } else {
58: // multiple callbacks in the method
59: for (int j = 0; j < argTypes.length; j++) {
60: Class<?> argClazz = argTypes[j];
61: if (argClazz.getName().equals(argument.getType())) {
62: // 将 ArgumentConfig 对象,添加到 `map` 集合中。
63: appendParameters(map, argument, method.getName() + "." + j); // `${methodName}.${index}`
64: if (argument.getIndex() != -1 && argument.getIndex() != j) { // 多余的判断,因为 `argument.getIndex() == -1` 。
65: throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument config error : the index attribute and type attribute not match :index :" + argument.getIndex() + ", type:" + argument.getType());
66: }
67: }
68: }
69: }
70: }
71: }
72: }
73: } else if (argument.getIndex() != -1) { // 指定单个参数的位置
74: // 将 ArgumentConfig 对象,添加到 `map` 集合中。
75: appendParameters(map, argument, method.getName() + "." + argument.getIndex()); // `${methodName}.${index}`
76: } else {
77: throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument config must set index or type attribute.eg: <dubbo:argument index='0' .../> or <dubbo:argument type=xxx .../>");
78: }
79:
80: }
81: }
82: } // end of methods for
83: }
84:
85: // generic、methods、revision
86: if (ProtocolUtils.isGeneric(generic)) {
87: map.put("generic", generic);
88: map.put("methods", Constants.ANY_VALUE);
89: } else {
90: String revision = Version.getVersion(interfaceClass, version);
91: if (revision != null && revision.length() > 0) {
92: map.put("revision", revision); // 修订号
93: }
94:
95: String[] methods = Wrapper.getWrapper(interfaceClass).getMethodNames(); // 获得方法数组
96: if (methods.length == 0) {
97: logger.warn("NO method found in service interface " + interfaceClass.getName());
98: map.put("methods", Constants.ANY_VALUE);
99: } else {
100: map.put("methods", StringUtils.join(new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(methods)), ","));
101: }
102: }
103: // token ,参见《令牌校验》http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/user/demos/token-authorization.html
104: if (!ConfigUtils.isEmpty(token)) {
105: if (ConfigUtils.isDefault(token)) {
106: map.put("token", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
107: } else {
108: map.put("token", token);
109: }
110: }
111: // 协议为 injvm 时,不注册,不通知。
112: if ("injvm".equals(protocolConfig.getName())) {
113: protocolConfig.setRegister(false);
114: map.put("notify", "false");
115: }
116: // export service
117: String contextPath = protocolConfig.getContextpath();
118: if ((contextPath == null || contextPath.length() == 0) && provider != null) {
119: contextPath = provider.getContextpath();
120: }
121:
122: // host、port
123: String host = this.findConfigedHosts(protocolConfig, registryURLs, map);
124: Integer port = this.findConfigedPorts(protocolConfig, name, map);
125:
126: // 创建 Dubbo URL 对象
127: URL url = new URL(name, host, port, (contextPath == null || contextPath.length() == 0 ? "" : contextPath + "/") + path, map);
128:
129: // 配置规则,参见《配置规则》http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/user/demos/config-rule.html
130: if (ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ConfiguratorFactory.class)
131: .hasExtension(url.getProtocol())) {
132: url = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ConfiguratorFactory.class)
133: .getExtension(url.getProtocol()).getConfigurator(url).configure(url);
134: }
135:
136: // 省略【服务暴露】逻辑
137: }第 2 至 6 行:协议名空时,缺省
"dubbo"。第 9 行:创建参数集合
map,用于下面创建 Dubbo URL 的parameters属性。第 10 至 15 行:将
sidedubbotimestamptimestamppid添加到map中。第 16 至 21 行:调用
#appendParameters(map, config)方法,将各种配置对象添加到map中。🙂
#appendParameters(map, config)方法,在 《API 配置(一)之应用》
第 22 至 83 行:调用 MethodConfig 对象数组,添加到
map中。目的是将每个 MethodConfig 和其对应的 ArgumentConfig 对象数组,添加到
map中。🙂 代码比较冗长,胖友耐心看注释,建议进行调试每种情况。
第 85 至 102 行:将
genericmethodsrevision到map中。revision,可能比较难理解,在 「10. Version」 详细解析。
第 103 至 110 行:将
token添加到map中。第 111 至 115 行:当协议为
injvm时,添加notify = false到map中,表示不注册,不通知。第 116 至 120 行:获得
contextPath,基础路径,即java web应用中常说的context path 。第 123 行:调用
#this.findConfigedHosts(protocolConfig, registryURLs, map)方法,获得注册到注册中心的服务提供者 Host 。指定服务注册地址,参见 dubbo-docker-sample 示例项目。
🙂 代码比较冗长,胖友耐心看注释,建议进行调试每种情况。
第 124 行:调用
#findConfigedHosts(protocolConfig, name, map)方法,获得注册到注册中心的服务提供者 Port 。🙂 代码比较冗长,胖友耐心看注释,建议进行调试每种情况。
第 127 行:创建 Dubbo URL 。
第 129 至 134 行:配置规则,后续详细解析。
第 136 行:省略【服务暴露】逻辑。
9. 为什么继承???
我们以 ServiceConfig 和 ProviderConfig 来举例子,两者都继承 AbstractServiceConfig。
从属性上,两者有相同的属性,例如 group / version 。
同时,也存在着一些差异,例如 ServiceConfig.interfaceName / ProviderConfig.host 。
另外,我们在看看 ServiceConfig 和 MethodConfig ,两者都继承 AbstractMethodConfig。
在 ServiceConfig 中,可以配置下属所有方法的 retries 次数,也可以在 MethodConfig 中自定义 retries 次数。
通过继承,获得相同的属性。
10. Version
Version#getVersion(cls, defaultVersion) 方法,获得版本号。代码如下:
1: public static String getVersion(Class<?> cls, String defaultVersion) {
2: try {
3: // find version info from MANIFEST.MF first
4: String version = cls.getPackage().getImplementationVersion();
5: if (version == null || version.length() == 0) {
6: version = cls.getPackage().getSpecificationVersion();
7: }
8: if (version == null || version.length() == 0) {
9: // guess version fro jar file name if nothing's found from MANIFEST.MF
10: CodeSource codeSource = cls.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource();
11: if (codeSource == null) {
12: logger.info("No codeSource for class " + cls.getName() + " when getVersion, use default version " + defaultVersion);
13: } else {
14: String file = codeSource.getLocation().getFile();
15: if (file != null && file.length() > 0 && file.endsWith(".jar")) {
16: file = file.substring(0, file.length() - 4);
17: int i = file.lastIndexOf('/');
18: if (i >= 0) {
19: file = file.substring(i + 1);
20: }
21: i = file.indexOf("-");
22: if (i >= 0) {
23: file = file.substring(i + 1);
24: }
25: while (file.length() > 0 && !Character.isDigit(file.charAt(0))) {
26: i = file.indexOf("-");
27: if (i >= 0) {
28: file = file.substring(i + 1);
29: } else {
30: break;
31: }
32: }
33: version = file;
34: }
35: }
36: }
37: // return default version if no version info is found
38: return version == null || version.length() == 0 ? defaultVersion : version;
39: } catch (Throwable e) {
40: // return default version when any exception is thrown
41: logger.error("return default version, ignore exception " + e.getMessage(), e);
42: return defaultVersion;
43: }
44: }第 3 至 7 行:从 MAINFEST.MF 中获得版本号。以 spring-boot-starter-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar 举例子: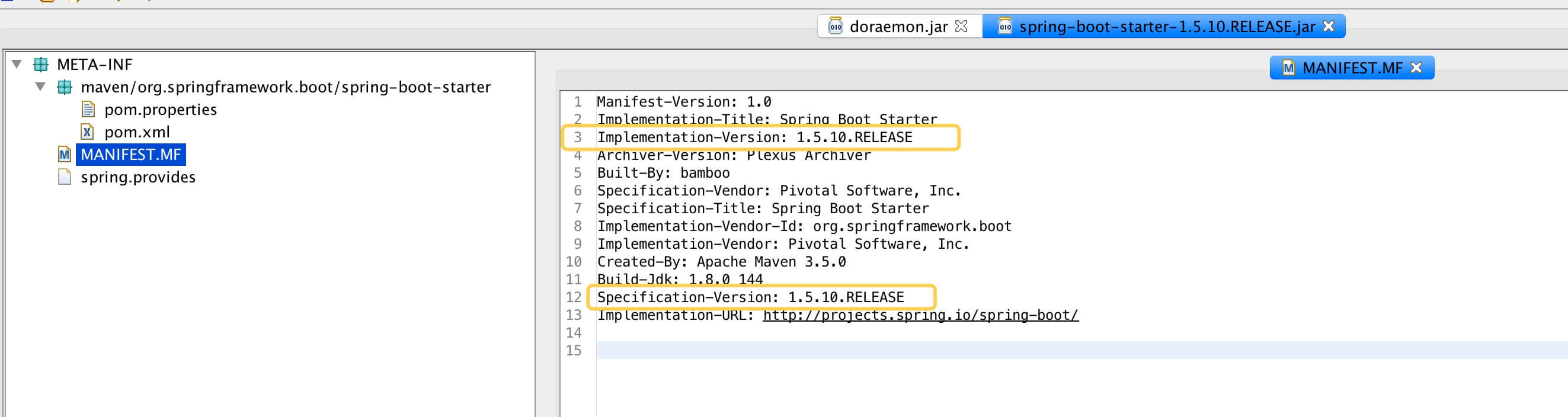
第 8 至 36 行:若获取不到,从 jar 包命名中可能带的版本号作为结果。例如上面的例子,
1.5.10.RELEASE。第 38 行:返回版本号。若不存在,返回默认版本号。